Vitamin D enhances your health in important ways, but unlike many other vitamins, it’s not available in a ton of foods. It’s important to recognize the signs of vitamin D deficiency and to take advantage of as many vitamin D health benefits as you can.

What is vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin, which means it dissolves in fat and is stored in your body’s tissues. It’s made by your body when your skin is exposed to sunlight and is also found in several foods and supplements. Generally, it’s recommended that you get 600 international units (IU) of vitamin D up to age 70 and 800 units if you’re older than 70.
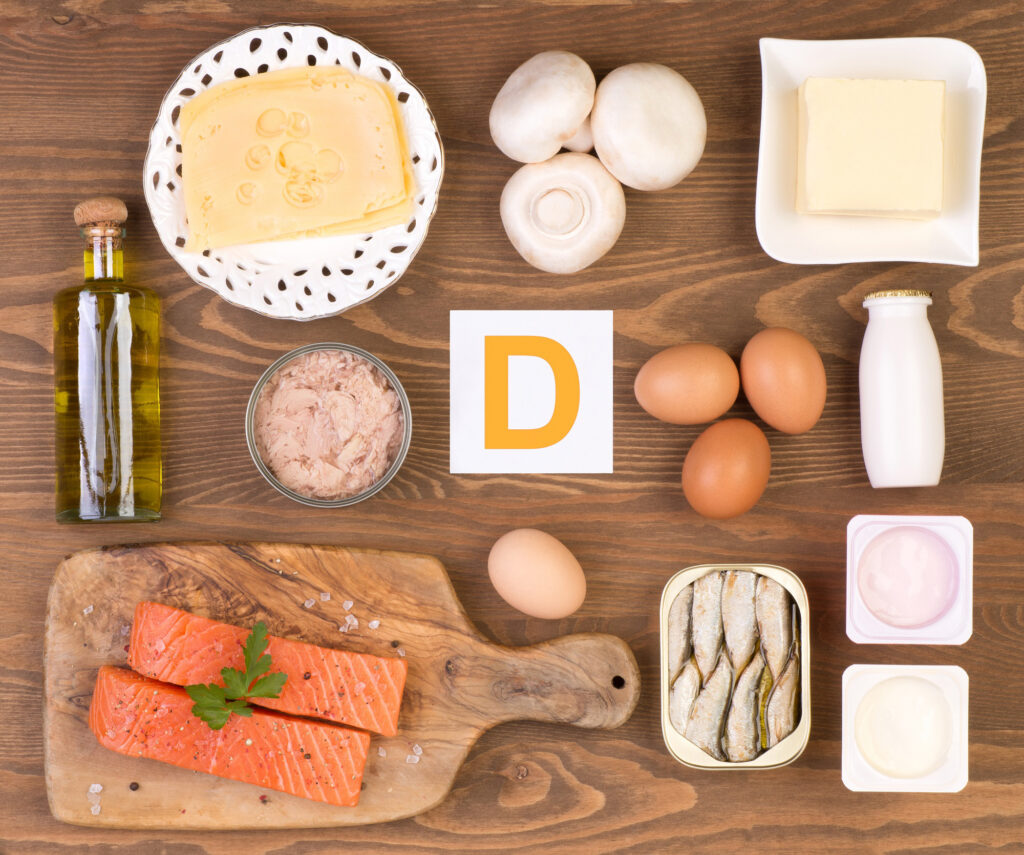

How can you get more of this vitamin?
Vitamin D is found in the following sources:
- Some types of fish, including swordfish, sockeye salmon, sardines and tuna
- Beef liver
- Fish liver oils
- Egg yolks
- Fortified products, such as orange juice, milk, yogurt, and cereal
- Sunshine (about 10 to 15 minutes a day, and you’ll need to dial down your use of sunscreen)
- Vitamin D supplements

What are some important vitamin D health benefits?
Vitamin D health benefits include:
- Regulating phosphorous levels in the blood: Phosphorous helps build and repair bones and teeth, facilitates nerve function and makes muscles contract.
- Absorbing calcium:Like phosphorous, this mineral helps build and repair bones and teeth, and facilitates nerve and muscle function. Calcium also assists in blood clotting and heart function.

What can happen if you’re deficient in vitamin D?
Not getting enough vitamin D has been associated with a number of health risks:
- Rickets, a disease characterized by soft bones and skeletal deformities
- Asthma in children
- Cancer
- An increased risk of death from heart and blood vessel disease
- Cognitive impairment in older adults

What puts you at a greater risk for vitamin D deficiency?
If you have any of these risk factors, you may want to talk to your doctor about your vitamin D levels:
- A vegan or similarly restrictive diet
- Low exposure to sunlight
- Obesity
- Dark skin (can reduce the amount of vitamin D your body makes when exposed to the sun)
- Certain medical issues such as Crohn’s disease and celiac disease, which can make your intestines less able to absorb vitamin D from the foods you eat
How do you know your body’s level of vitamin D?
Your doctor can test your blood to measure the levels of vitamin D in your body. If you’re deficient, you may be advised to take a supplement, eat foods that have high levels of vitamin D and/or spend more time in the sun.
To learn more about maximizing vitamin D health benefits and other ways you can improve your health, contact BMI of Texas.
You might also be interested in: The Skinny on Artificial Sweeteners

