For overweight young adults, extra pounds can take a significant physical and mental toll on your well-being over the years. Unfortunately, these young adults often develop weight-related problems due to being overweight as children or adolescents. Carrying extra weight for decades can result in an increased risk of developing many serious and chronic health issues. However, there are solutions, such as the gastric bypass surgery, which can help impact and reduce these problems.
What are the negative effects of extra weight?
Obesity has reached epic proportions in the U.S., affecting over one-third of adults, according to statistics from the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). It also affects many young people, with about 17% or 12.7 million children and adolescents age 2 to 19 having obesity. Many of them continue to have the following weight-related issues throughout young adulthood and beyond:
- High blood pressure
- Type 2 diabetes
- Stroke
- Coronary heart disease
- Gallbladder disease
- Cancers – such as those that affect the breast, prostate and colon
- Sleep apnea
- Respiratory problems
- Lower self-esteem
- Depression
- Social stigma
- Discrimination
Just as the reasons for weight gain can be varied, it can also be difficult and sometimes complicated to lose weight in a healthy way and keep it off. Doctors may tell their patients they’re overweight and need to eat a healthier diet and get more exercise, but this is far easier said than done.
And unfortunately, the effects of being overweight can make these healthier choices more difficult to begin and maintain. For example, if you’re obese, you’ll have an increased risk of depression. This can make you more likely to overeat and to reach for sweets or carbohydrates. You’ll also probably feel lethargic and will be less likely to exercise or live an active lifestyle. In this vicious cycle, you’ll gain even more weight.
Therefore, losing weight and keeping it off can be extremely frustrating and difficult, resulting in one failed diet after another or an unhealthy cycle of weight loss and gain. As a result, many people have turned to weight loss surgery – particularly gastric bypass – as a tool to help them lose weight.
Gastric bypass surgery has been performed since 1968, and it’s been improved and refined since then. Today, it accounts for nearly half of all weight loss surgeries, so it has a strong track record of data as well as positive results over the years.
The following information from BMI of Texas explains what you need to know about whether gastric bypass surgery can be appropriate for overweight young adults, as well as how it can impact morbidity and mortality rates:
What are the benefits of gastric bypass?
Gastric bypass surgery can be a useful tool in accelerating weight loss. It changes your body in several ways that make weight loss much easier and quicker. This surgery gives young adults many of the same benefits that it provides for older patients, but the positive effects may be even greater.
That’s because if you have the surgery and lose excess weight as a young adult, you’re able to avoid additional years of health concerns. This can help reduce what’s known as morbidity and mortality – with morbidity referring to a diseased state and mortality referring to the rate of death. In other words, gastric bypass surgery may be able to help young adults lead longer, healthier lives.
In one study, a group of young adults who had gastric bypass or laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy between the ages of 18 and 24 were questioned 6 months to 6 years after their surgery. Gastric bypass patients were able to achieve an average mean weight loss of 35.6%. The study also found that young adults may need additional support to help them continue their behavioral changes post-operatively, since adherence tended to slip over the years.
Gastric bypass offers young adults the following benefits:
- Results in rapid, significant, long-term weight loss
- Reduces the risk or severity of, or even eliminates, many present and future physical and mental health problems
- Is as safe and effective in young adults as it is in adults
- Long history of proven results
What’s involved with gastric bypass surgery?
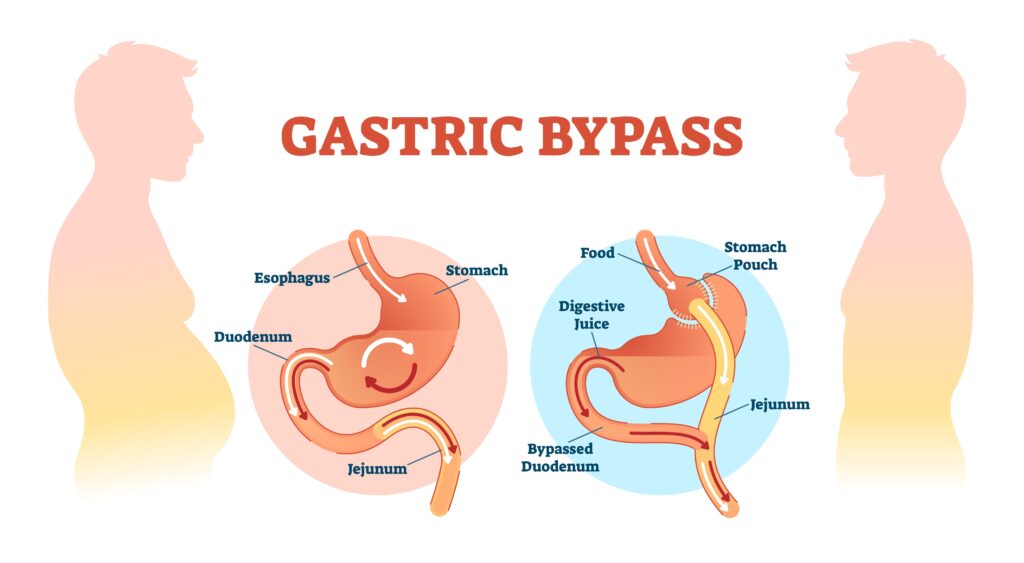
If you’re having gastric bypass surgery, it will be performed in two parts. In the first, your stomach will be divided into two portions, where one portion is much larger than the other. The smaller part is then sewn or stapled together to create a new, smaller, stomach. This new “pouch” holds only about an ounce of food, so you’ll feel full much more quickly and will eat less.
In the second part of the surgery, your surgeon will then disconnect your new, small stomach pouch from the rest of your stomach and the first part of the small intestine (duodenum). In a surgical technique known as a Roux-en-Y, the pouch will then be connected to a part of the small intestine that’s slightly farther down (in the jejunum). This allows food to go from your stomach into the jejunum and bypass the duodenum. As a result, your body will absorb fewer calories (and nutrients) which is why you’ll need to continue to take vitamin and mineral supplements for the rest of your life.
In addition to making you feel fuller, faster when eating, the surgery also alters your body’s neurochemical pathways and hormones so you lose weight more rapidly. You’ll have better control over your blood sugars, which has been linked to many different chronic diseases.
What happens after surgery?
Gastric bypass surgery can usually be performed laparoscopically, which means your surgeon can make smaller cuts. As a result, your hospital stay will be shorter, and you’ll recover more quickly. On average, patients whose gastric bypass surgery is performed in this way stay in the hospital for 2 to 3 days and after 3 to 5 weeks can resume normal activities. If your surgeon must use larger cuts in what’s called “open” surgery, your recovery time will be longer.
As with any surgery, there can be risks and complications, but most people experience no serious problems. Only about 10% of people have any complications at all, the clear majority of which are minor. Common, non-serious side effects can include constipation or gallstones. Rarer side effects can include bleeding in the stool or a blood clot in the lung, although the latter can typically be prevented by being active and using blood-thinning medication after surgery.
What should you consider before having gastric bypass surgery?
Weight loss surgery isn’t considered to be the best first choice to try to lose weight. It’s usually an option only after you haven’t been able to lose or sustain weight loss after changing your lifestyle habits. You’ll also need to have a clear understanding of the surgery and what will be expected of you after your procedure.
First, it’s important to note that gastric bypass surgery isn’t appropriate if you don’t have much weight to lose. To have this procedure, you’ll need to have a minimum body mass index (BMI) of 35, or possibly 40, depending on your individual circumstances. As a frame of reference, a person with a BMI of 40 probably carries about 235 pounds if he or she is 5 feet 4 inches tall and a weight about 280 pounds if he or she is 5 feet 10 inches tall.
To achieve the best possible results, you’ll need to make healthier lifestyle choices after your surgery. For example, you should increase your intake of protein and limit the foods you eat that are high in sugar and refined carbohydrates. Since foods high in sugar and/or refined carbohydrates often cause a post-surgery effect known as dumping syndrome, you’ll find it easier to avoid these triggers. Foods such as these can cause symptoms such as nausea, weakness, and sweating, so if this starts to happen, you probably won’t find yourself craving these unhealthy foods.
The way you eat will also need to change. As you gained weight, you may have eaten large portions or even binged on certain foods. After gastric bypass surgery, you’ll need to eat smaller meals more frequently that your stomach can handle. Additionally, because your body may not get enough vitamins and minerals from these smaller meals after your surgery, you’ll have to commit to taking a multi-vitamin as well as calcium and B12 supplements for the rest of your life. Combining better eating habits with regular exercise will help you keep weight off in the long-term, and exercising should become easier as you lose weight.
One of the most difficult challenges post-surgery will be learning how to combat stressful situations. If stress eating was a coping mechanism prior to having gastric bypass, you’ll also need to find a productive way to deal with stress and anxiety. To help overcome these poor coping mechanisms and deal with stress positively, a BMI of Texas Behavioral Health Specialist is available to support you before and after surgery.
A young adult should weigh the potential risks and post-surgery requirements involved with gastric bypass surgery along with the potential results. You’ll need to be physically and psychologically prepared not only for the surgery itself, but for the recovery and healthy habits that need to be formed. It’s an important decision, and it’s also vital to realize that the changes you’ll undergo will begin, not end, when the surgery is complete.
If you’re one of the many overweight young adults who’s struggling with obesity and wants to find out more about gastric bypass and other weight loss options, contact BMI of Texas today at 210-405-6424. Our experienced doctors will make a recommendation based on your unique needs and circumstances, and we’ll set up support such as a nutrition team to help you succeed with your post-surgery goals should you choose gastric bypass. We even have a fitness center where every piece of equipment has been built for bariatric patients. We’ll do everything we can to help you succeed in achieving a healthier lifestyle!

